Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is location-independent computing, whereby shared servers provide resources, software, and data tocomputers and other devices on demand, as with the electricity grid.source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
Cloud Computing as the term indicates implies using the cloud infrastructure or internet based shared infrastructure to host and access applications. That means hosting application and their data on a shared servers on the internet and access the applications through a browser.
Things that cloud computing change
- Completely shift from Desktop based model to Web based model. In cloud computing model applications are web based hosted on a cloud server and users can access the applications through a web browser.
- Hosting application and services. Today most business organizations host application on their servers and use their firewalls. So adding these things is a extra overhead for organizations. Moving to the cloud model make it easier to organizations.
- Security, a key implication in cloud computing is that security risk added by the third party provider.
Saas, Paas and Iaas
Cloud computer has various flavors of implementation. In
here we talk about SaaS(Software as a Service) , PaaS(Platform as a
service), IaaS(Infrastructure as a service).
Software as a Service (Saas)
This term describe software that is deployed over the
internet. The services are provided with typically payment charged on
monthly basis based on the number of users or services consumed.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Provide the ability for building and deploying custom application on their platform.
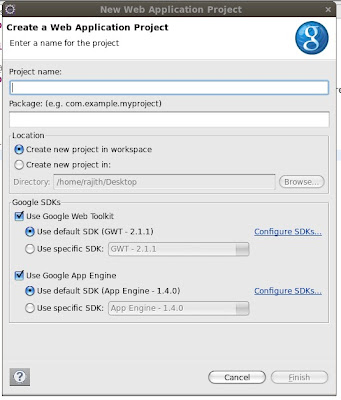
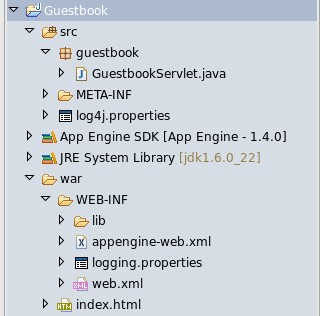
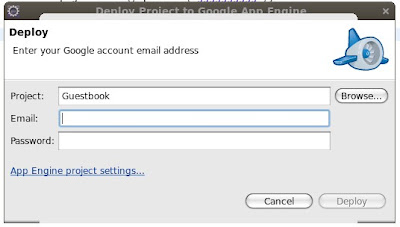
Amazon EC2 , Microsoft Azure , Google App Engine are some of service providers.
Infrastructure as a service (Iaas)
Provide computer and server infrastructure as a virtualization environment.
Amazon Web Services and Rackspace are examples of service provides.
Here is the brief description about cloud computing.