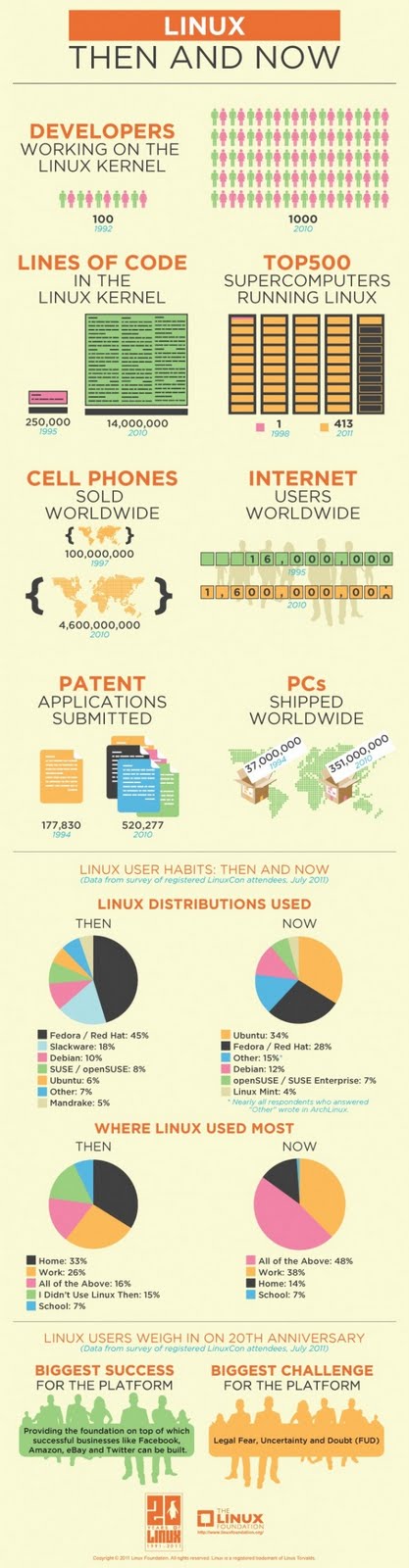
LINUX NETWORKING COMMANDS
Linux is most powerful operating system which often needs to use
commands
to explore it effectively.Some of the commands are restricted to normal
user groups as they are powerful and has more functionality involved in
it.Here we summarized most interesting and useful networking commands
which every linux user are supposed to be familiar with it.
1.Arp
manipulates the kernel’s ARP cache in various ways. The primary options
are clearing an address mapping entry and manually setting up one. For
debugging purposes, the arp program also allows a complete dump of the
ARP cache.ARP displays the IP address assigned to particular ETH card
and mac address
[fasil@smashtech ]# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
59.36.13.1 ether C eth0 |
2.Ifconfig
is used to configure the network interfaces. Normally we use this
command to check the IP address assigned to the system.It is used at
boot time to set up interfaces as necessary. After that, it is usually
only needed when debugging or when system tuning is needed.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# /sbin/ifconfig
eth0 UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:126341 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:44441 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
3. Netstat
prints information about the networking subsystem. The type of
information which is usually printed by netstat are Print network
connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade
connections, and multicast.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# netstat
Active Internet connections (w/o servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 .230.87:https ESTABLISHED
Active UNIX domain sockets (w/o servers)
Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path
unix 10 [ ] DGRAM 4970 /dev/log
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 6625 @/var/run/hal/hotplug_socket
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 2952 @udevd
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 100564
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 62438 /tmp/.X11-unix/X0
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 62437
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 10271 @/tmp/fam-root-
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 10270
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 9276
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 9275
4.ping
command is used to check the connectivity of a system to a
network.Whenever there is problem in network connectivity we use ping to
ensure the system is connected to network.
[root@smashtech ~]# ping google.com
PING google.com (74.125.45.100) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from yx-in-f100.google.com (74.125.45.100): icmp_seq=0 ttl=241 time=295 ms
64 bytes from yx-in-f100.google.com (74.125.45.100): icmp_seq=1 ttl=241 time=277 ms
64 bytes from yx-in-f100.google.com (74.125.45.100): icmp_seq=2 ttl=241 time=277 ms
--- google.com ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 6332ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 277.041/283.387/295.903/8.860 ms, pipe 2
5.Nslookup
is a program to query Internet domain name servers. Nslookup has two
modes: interactive and non-interactive. Interactive mode allows the user
to query name servers for information about various hosts and domains
or to print a list of hosts in a domain. Non-interactive mode is
used to print just the name and requested information for a host or
domain.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# nslookup google.com
Server: server ip
Address: gateway ip 3
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: google.com
Address: 209.85.171.100
Name: google.com
Address: 74.125.45.100
Name: google.com
Address: 74.125.67.100
6. dig
(domain information groper) is a flexible tool for interrogating DNS
name servers. It performs DNS lookups and displays the answers that
are returned from the name server(s) that were queried. Most DNS
administrators use dig to troubleshoot DNS problems because of its
flexibility, ease of use and clarity of output. Other lookup tools tend
to have less functionality than dig.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# dig google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.2.4 <<>> google.com
;; global options: printcmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 4716
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 4, ADDITIONAL: 4
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;google.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
google.com. 122 IN A 74.125.45.100
google.com. 122 IN A 74.125.67.100
google.com. 122 IN A 209.85.171.100
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
google.com. 326567 IN NS ns3.google.com.
google.com. 326567 IN NS ns4.google.com.
google.com. 326567 IN NS ns1.google.com.
google.com. 326567 IN NS ns2.google.com.
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
ns1.google.com. 152216 IN A 216.239.32.10
ns2.google.com. 152216 IN A 216.239.34.10
ns3.google.com. 152216 IN A 216.239.36.10
ns4.google.com. 152216 IN A 216.239.38.10
;; Query time: 92 msec
;; SERVER: 172.29.36.1#53(172.29.36.1)
;; WHEN: Thu Mar 5 14:38:45 2009
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 212
7.Route
manipulates the IP routing tables. Its primary use is to set up static
routes to specific hosts or networks via an interface after it has
been configured with the ifconfig program.When the add or del options
are used, route modifies the routing tables. Without these options,
route displays the current contents of the routing tables.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
54.192.56.321 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
* 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
default 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
8.Traceroute
: Internet is a large and complex aggregation of network hardware,
connected together by gateways. Tracking the route one’s packets follow
(or finding the miscreant gateway that’s discarding your packets)
can be difficult.
Traceroute utilizes the IP protocol ‘time to live’ field and attempts to
elicit an ICMP TIME_EXCEEDED response from each gateway along the path
to some host. The only mandatory parameter is the destination host name
or IP number. The default probe datagram length is 40 bytes, but
this may be increased by specifying a packet length (in bytes) after the
destination host name.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# traceroute google.com
traceroute: Warning: google.com has multiple addresses; using 209.85.171.100
traceroute to google.com (209.85.171.100), 30 hops max, 38 byte packets
1 * * *
9.W-displays
information about the users currently on the machine, and their
processes. The header shows, in this order, the current time, how long
the system has been running, how many users are currently logged on,
and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
[fasil@smashtechl ~]# w
15:18:22 up 4:38, 3 users, load average: 0.89, 0.34, 0.19
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root :0 - 10:41 ?xdm? 24:53 1.35s /usr/bin/gnome-session
root pts/1 :0.0 10:58 1.00s 0.34s 0.00s w
root pts/2 :0.0 12:10 23:32 0.03s 0.03s bash
10. Nmap
is designed to allow system administrators and curious individuals to
scan large networks to determine which hosts are up and what services
they are offering. nmap supports a large number of scanning
techniques such as:UDP, TCP connect(), TCP SYN (half open), ftp
proxy (bounce attack), ICMP (ping sweep), FIN, ACK sweep, Xmas Tree,SYN
sweep, IP Protocol, and Null scan. See the Scan Types section for more
details. nmap also offers a number of advanced features such as
remote OS detection via TCP/IP fingerprinting, stealth scanning,
dynamic delay and retransmission calculations, parallel scanning,
detection of down hosts via parallel pings, decoy scanning, port
filtering detection, direct (non-portmapper) RPC scanning,
fragmentation scanning, and flexible target and port specification.
Significant effort has been put into decent nmap performance for
non-root users. Unfortunately, many critical kernel interfaces (such
as raw sockets) require root privileges. nmap should be run as root
whenever possible (not setuid root, of course).
The result of running nmap is usually a list of interesting ports
on the machine(s) being scanned (if any). Nmap always gives the
port’s "well known" service name (if any), number, state, and
protocol. The state is either"open", "filtered", or "unfiltered". Open
means that the target machine will accept() connections on that
port.Filtered means that a firewall, filter, or other network
obstacle is covering the port and preventing nmap from determining
whether the port is open. Unfiltered means that the port is known by
nmap to be closed and no fire-wall/filter seems to be interfering
with nmap’s attempts to determine this. Unfiltered ports are the common
case and are only shown when most of the scanned ports are in the
filtered state.
Depending on options used, nmap may also report the following
characteristics of the remote host: OS in use, TCP sequentiality,
usernames running the programs which have bound to each port, the DNS
name, whether the host is a smurf address, and a few other--Network
exploration tool and security scanners.
[fasil@smashtech ~]# nmap 52.194.69.152
Starting nmap 3.70 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2009-03-05 15:21 IST
Interesting ports on 52.194.69.152
(The 1658 ports scanned but not shown below are in state: closed)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
111/tcp open rpcbind