Future and Past of Linux Then and Now


package rd.test;
public class DynamicTest {
private int count;
public void printStar() {
System.out.println("*");
}
public void printStarWithInt(int i) {
System.out.println("* Integer : " + i);
}
public void printStarWithString(String param) {
System.out.println("* String : " + param);
}
public void printStarWithStrings(String param1, String param2) {
System.out.println("* String : " + param1 + " , and " + param2);
}
private void printStarInPrivate() {
System.out.println("* Private : *");
}
}
package rd;
import rd.test.DynamicTest;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException,
InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class cls = Class.forName("rd.test.DynamicTest");
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
/**
* calling printstart method without passing any parameters
* */
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("printStar", null);
method.invoke(obj, null);
/**
* calling printStarWithInt method with int parameter
*/
Class[] intParam = new Class[1];
intParam[0] = Integer.TYPE;
method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("printStarWithInt", intParam);
method.invoke(obj, 100);
/**
* calling printStarWithStrings methos with two string parameters
*/
Class[] stringParams = new Class[2];
stringParams[0]=String.class;
stringParams[1]=String.class;
method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("printStarWithStrings", stringParams);
method.invoke(obj, "hi","rajith");
/**
* calling private method in DynamicTest class
*/
method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("printStarInPrivate", null);
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(obj, null);
/**
* setting and getting private fileds
*/
DynamicTest dynamicTest = new DynamicTest();
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("count");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.setInt(dynamicTest,10);
System.out.println(field.get(dynamicTest));
}
}
package rd.domain;
public class Message {
private String description;
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
package rd.concurent;
import rd.domain.Message;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class Producer implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<Message> queue;
public Producer(BlockingQueue<Message> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// create messages and adding to queue
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
Message message = new Message();
message.setDescription(" Message " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(i);
queue.put(message);
System.out.println("Produced " + message.getDescription());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// adding exit message
Message message = new Message();
message.setDescription("finish");
try {
queue.put(message);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package rd.concurent;
import rd.domain.Message;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<Message> queue;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue<Message> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Message message = null;
try {
while (!(message = queue.take()).getDescription().endsWith("finish")){
Thread.sleep(10);
System.out.println("Consumed " + message.getDescription());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package rd;
import rd.concurent.Consumer;
import rd.concurent.Producer;
import rd.domain.Message;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Message> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
Producer producer = new Producer(blockingQueue);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(blockingQueue);
new Thread(consumer).start();
new Thread(producer).start();
System.out.println("Started.................");
}
}
I like my code to be elegant and efficient. The logic should be straightforward to make it hard
for bugs to hide, the dependencies minimal to ease maintenance, error handling complete
according to an articulated strategy, and performance close to optimal so as not to tempt
people to make the code messy with unprincipled optimizations. Clean code does one thing
well.
Clean code can be read, and enhanced by a developer other than its original author. It has
unit and acceptance tests. It has meaningful names. It provides one way rather than many
ways for doing one thing. It has minimal dependencies, which are explicitly defined, and provides a clear and minimal API. Code should be literate since depending on the language, not all necessary information can be expressed clearly in code alone.
I could list all of the qualities that I notice in clean code, but there is one overarching quality that leads to all of them. Clean code always looks like it was written by someone who cares. There is nothing obvious that you can do to make it better. All of those things were thought
about by the code’s author, and if you try to imagine improvements, you’re led back to
where you are, sitting in appreciation of the code someone left for you—code left by someone
who cares deeply about the craft.
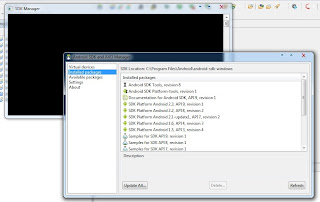
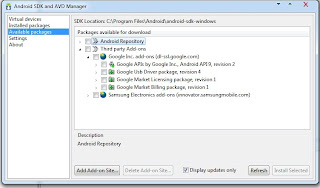
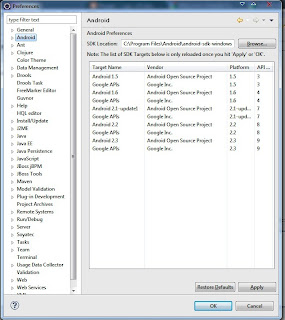
Cloud computing is location-independent computing, whereby shared servers provide resources, software, and data tocomputers and other devices on demand, as with the electricity grid.source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
mysqldump -u root -p[root_mysql_password] [database_name] > [path_to_save_with_sql_extension]
ex:
mysqldump -u root -p123 test > D:/backups/test_backup.sql
mysqldump -u root -p[root_mysql_password] --databases [database_name] [database_name] .. > [path_to_save_with_sql_extension]
ex:
suppose we have two databases called test and tutorial
mysqldump -u root -p123 --databases test tutorial > D:/backups/test_tutorial.sql
mysqldump -u root -p[root_mysql_password] -all-databases > [path_to_save_with_sql_extension]
Suppose we have a demo table in test database.
mysqldump -u root -p123 test demo \ > D:/backups/demotables.sql
mysql -u root -p[root_mysql_password] [database_name] < D:/backups/test.sql